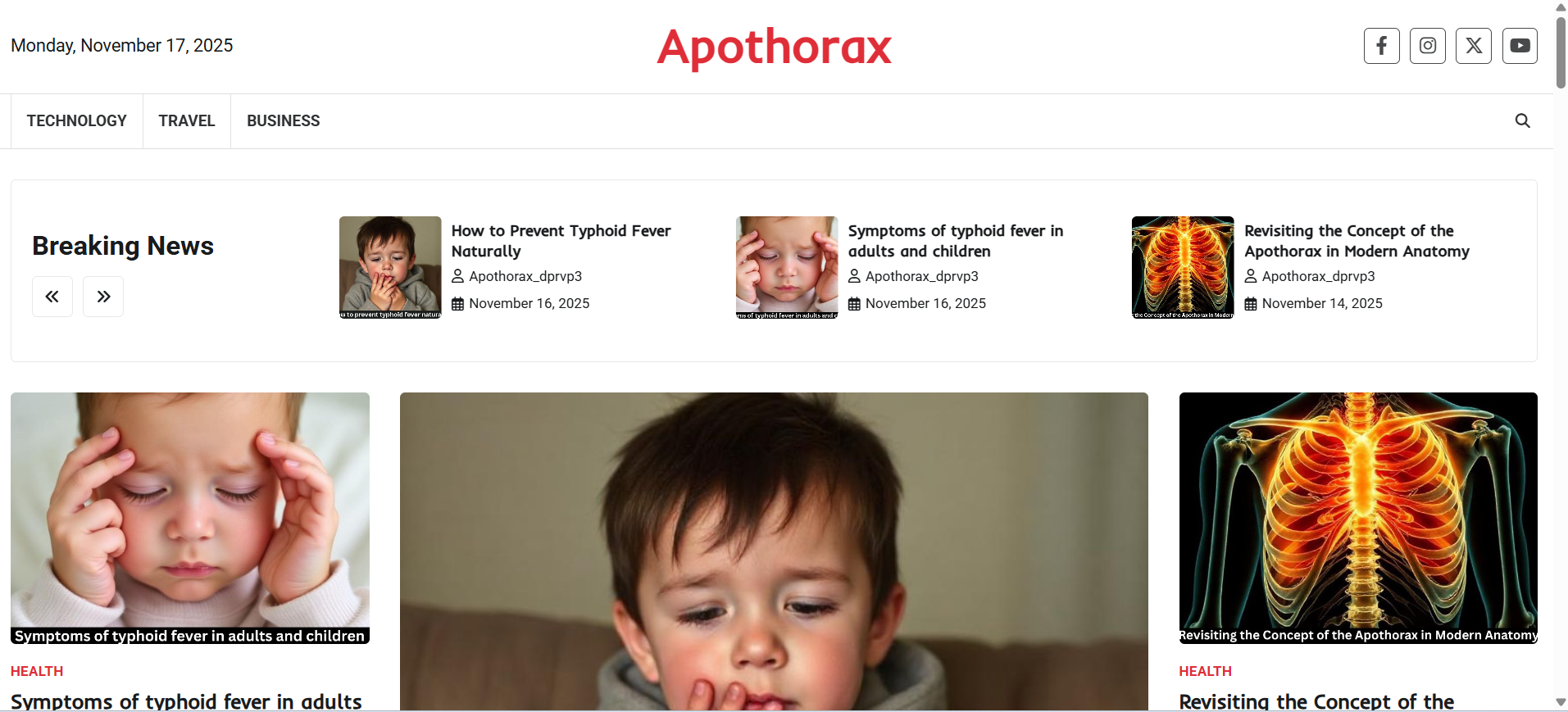
If there’s one set of terms guaranteed to confuse students, it’s apothorax, mesothorax, and metathorax. Why? Because one belongs to human anatomy and the other two belong entirely to insect anatomy. Understanding the difference can instantly clear up confusion and make your biology revision much easier.
Why These Terms Are Often Confused
All three contain the word “thorax,” so many assume they refer to the human chest. But in reality, mesothorax and metathorax belong to insects, while apothorax is a lesser-known concept in human anatomy.
Importance of Understanding Thoracic and Insect Anatomy Terminology
These terms appear in both human and comparative anatomy chapters—making it crucial to distinguish them clearly.
What Is the Apothorax?
Basic Definition
The apothorax refers to the supportive region surrounding the human thorax, especially near the lower lateral chest wall.
Etymology and Meaning
- “Apo” = around/supporting
- “Thorax” = chest
So apothorax means “around the chest.”
Where the Term Is Used
It appears in descriptive human anatomy, older textbooks, and comparative anatomical discussions.
What Is the Mesothorax?
Meaning and Location in Insects
The mesothorax is the middle segment of the insect thorax. Insects have three thoracic segments:
- Prothorax
- Mesothorax
- Metathorax
Major Structures Found in the Mesothorax
The mesothorax typically includes:
- The forewings
- Second pair of legs
- Powerful flight muscles
- Spiracles (in some species)
Its Functional Importance
The mesothorax plays a major role in:
- Wing movement
- Flight stability
- Support for locomotion
What Is the Metathorax?
Location and Definition
The metathorax is the third (rear) segment of the insect thorax.
Structures Found in the Metathorax
It contains:
- Hindwings
- Third pair of legs
- Large indirect flight muscles
- Important nerve connections
Functional Role in Insect Physiology
The metathorax is essential for:
- Secondary wing function
- Jumping or climbing movement (in some insects)
- Advanced flight maneuvering
Structural Differences
Apothorax vs. Mesothorax
- Apothorax = human support region
- Mesothorax = insect’s second thoracic segment responsible for flight
Mesothorax vs. Metathorax
- Mesothorax = forewings + second legs
- Metathorax = hindwings + third legs
Apothorax vs. Metathorax
- Apothorax: Not a true anatomical cavity and found only in humans
- Metathorax: Specialized insect segment designed for movement and wing control
Functional Differences
Supportive Function of the Apothorax
- Supports rib movement
- Protects thoracic organs
- Stabilizes the chest wall
Flight-Related Functions of the Mesothorax
- Forewing movement
- Stronger flight muscle attachment
Locomotion and Wing Movement in the Metathorax
- Hindwing motion
- Jumping and complex movement in some species
Comparative Anatomy Overview
Human Anatomy vs. Insect Anatomy
Humans have a single thorax, while insects have a three-part thorax.
Why These Terms Cannot Be Interchanged
- Apothorax = human supportive tissue
- Mesothorax & metathorax = insect body segments
Key Biological Distinctions
Insects use their thorax for locomotion and flight, while humans use it to protect organs and support respiration.
Why Understanding These Differences Matters
Academic Significance
Appears in exam questions, particularly in class 11/12 biology and competitive exams.
Use in Comparative Anatomy
Helps students compare structural adaptations in humans vs insects.
Importance for Biology Students
Prevents confusion and strengthens conceptual clarity.
Common Misconceptions
Confusing Apothorax With Insect Thoracic Segments
They are completely unrelated.
Misinterpreting Mesothorax and Metathorax Locations
Many students reverse their order.
Assuming All Terms Refer to Human Anatomy
Only apothorax relates to humans.
Quick Revision Chart
| Term | Belongs To | Meaning | Key Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apothorax | Humans | Region around thorax | Support & protection |
| Mesothorax | Insects | Middle thoracic segment | Forewing movement |
| Metathorax | Insects | Third thoracic segment | Hindwing & locomotion |
Memorization Tips
Mnemonics
“Pro-Me-Meta” = insect thorax order
“Apo = around” = apothorax surrounds human thorax
Visual Learning
Use diagrams of insects vs humans for clarity.
Concept-Based Recall
Remember this:
Humans protect; insects fly.
Conclusion
The apothorax, mesothorax, and metathorax may sound similar, but they belong to two different worlds—humans and insects. Understanding their differences not only sharpens your anatomical knowledge but also helps you excel in biology exams. Whether it’s supporting the lungs in humans or powering flight in insects, each term plays a unique role in anatomy and physiology.
FAQs
1. Is the mesothorax found in humans?
No, it is only found in insects.
2. Does the apothorax contain organs?
No, it contains supportive muscles and tissues around the thorax.
3. Which segment of insects contains the hindwings?
The metathorax.
4. What is the function of the mesothorax?
It primarily supports forewing movement and locomotion.
5. Why is it important to distinguish these terms?
Because they refer to completely different anatomical structures in humans vs insects.